上一篇 post 记录了 OpenCV 的编译脚本,当然是因为马上会用到啦~在 Rust 中要用 OpenCV 的话,则是需要用到 twistedfall/opencv-rust 这个 binding。使用方法其实倒也蛮简单,只不过 Rust 里面的函数没有参数默认值这个东西,于是在Rust 里使用 OpenCV 函数的时候,还能顺便记忆 OpenCV 里函数都有哪些参数╮( ̄▽ ̄"")╭
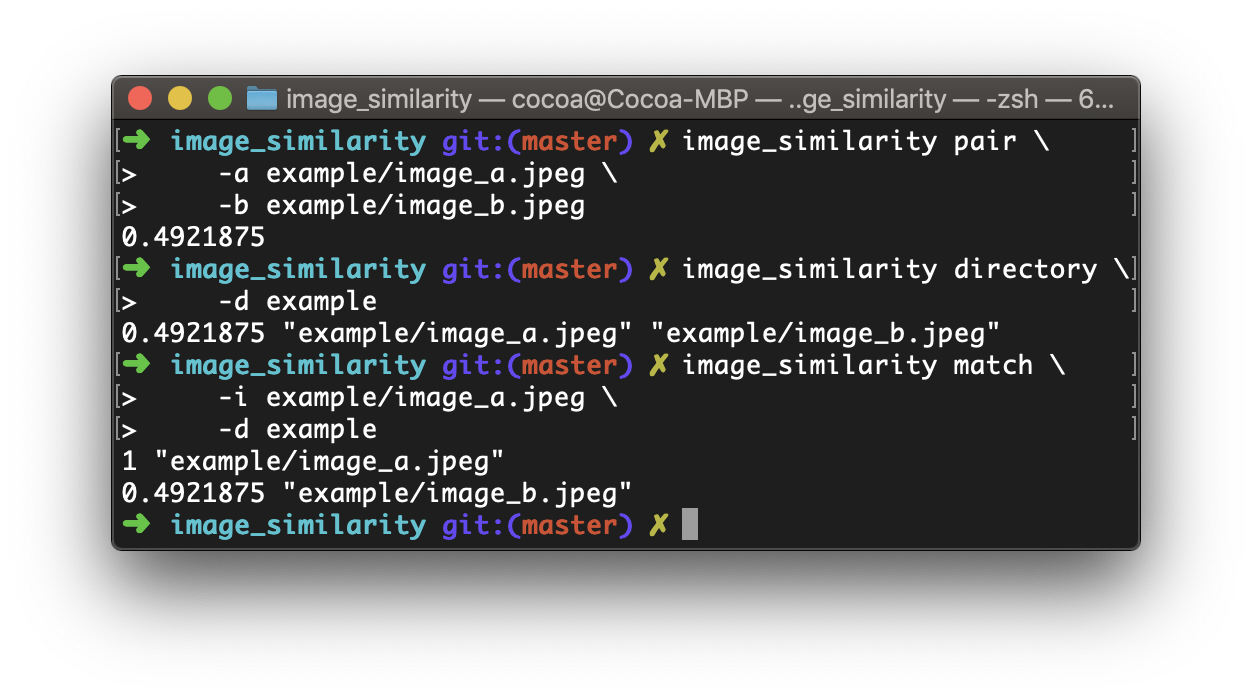
在有了图像相似度之后,就可以做比如查找某一目录下是否有重复的图片之类的,或者给出一张图,查找某个目录下与它最相似的图片等等~
计算方法
当然话说回来,计算图像相似度本身是有很多种方法的,这里因为学习 Rust 为主要目的,于是暂且不在计算方法上做什么创新。后文中使用到的计算图像相似度的算法与参数取自 MoeOverflow 组织 @Shincurry 的 AnimeLoop 项目,详细的参数选择解释可以在 Shincurry 的博客里找到~ https://blog.windisco.com/animeloop-paper/
简单来说,我们会将图片转化为灰度图,然后缩放到 64x64 的大小,并转换其底层的数据类型为 f64,随后计算其相应的离散余弦变换「Discrate Cosine Transform」。
接着取离散余弦变换结果矩阵的左上 $16\times 16$ 的子矩阵,计算其均值,需要注意的是,$(0, 0)$ 的值要排除在外。因为 $(0, 0)$ 是其直流分量「DC coefficient」,如果用来计算平均值的话,则可能会明显影响计算结果。那么在计算平均值的时候的总个数就是 $16 \times 16 - 1$。
在有了左上角 $16 \times 16$ 矩阵的均值 $m$ 之后,就可以依次将这个 $16 \times 16$ 矩阵的每一个元素 $v_{(p, q)}$ 与 $m$ 相比较,如果 $v_{(p, q)} \lt m$,那么 pHash 字符串就最末尾增加 "1";否则则增加 "0"
在有了两张图片的 pHash 字符串 $\mathcal{A}, \mathcal{B}$ 之后,我们计算两个 pHash 的汉明距离「Hamming Distance」 $d$,然后相似度则为 $r = 1.0 - \frac{d}{l}$,其中 $l$ 为 pHash 字符串长度。
\begin{align} &d = 0\\ &l = 16\times 16\\ & \forall i \in [0, 16\times 16)\\ & \left\{ \begin{aligned} d = d + 1, &\, \mathcal{A}_i \lt \mathcal{B}_i\\ d = d + 0, &\, \mathcal{A}_i \ge \mathcal{B}_i \end{aligned} \right.\\ &r = 1.0 - \frac{d}{l} \end{align}Rust 代码
其实在理清楚思路之后就蛮简单了,不过因为 Rust 的 OpenCV binding 是自动生成的,所以需要时不时查阅一下其源代码。
因为 C++ 的 OpenCV 里面有很多默认参数,在生成 Rust 代码时,这些带有默认参数的函数被重命名了,因此直接对应上 Rust 里的函数还是有点麻烦。好在 Rust 的 crate 网站上可以直接找到所有的函数、module、struct 等等,直接在上面查找还是很方便的~ https://docs.rs/opencv
. ├── Cargo.toml └── src ├── image_similarity │ ├── error.rs │ ├── image_similarity.rs │ └── mod.rs └── main.rs
error.rs 是定义了一个 ImageSimilarityError 的 struct,用于把 OpenCV 的 Error 类型和我们计算时可能有的 Error 合在一个类里。
image_similarity.rs 就是本体了,最后由 mod.rs 将几个计算相似度的函数和 ImageSimilarityError 导出到 image_similarity:: 下。
main.rs 的话,还是用了 clap 来做 cli 参数的 parse,clap 这个 crate 确实蛮好用的~♪(´ε` )
项目的源代码在我的 GitHub 上,#/image-similarity ~这里就只贴一下重点的 image_similarity.rs 好了~
use opencv::core::{Mat, Scalar, Size_, dct, CV_64FC1}; use opencv::imgcodecs::imread; use opencv::imgproc::{self, cvt_color, resize, COLOR_RGB2GRAY, COLOR_RGBA2GRAY}; use super::error::ImageSimilarityError; use walkdir::WalkDir; /// Compute the similarity of two given image /// /// # Example /// ```rust /// let image_a = opencv::imgcodecs::imread("/PATH/TO/IMAGE/A", 0).expect("Invaild image file a"); /// let image_b = opencv::imgcodecs::imread("/PATH/TO/IMAGE/B", 0).expect("Invaild image file b"); /// match similarity(&image_a, &image_b, 64, 16) { /// Ok(similarity) => println!("{}", similarity), /// Err(e) => println!("{}", e), /// } /// ``` pub fn similarity(img_a: &Mat, img_b: &Mat, length: i32, dct_length: i32) -> Result<f64, ImageSimilarityError> { // of course length and dct_length should be greater than 0 if length <= 0 { return Err(ImageSimilarityError { reason: format!("length should be a positive number instead of {}", length)}) } if dct_length <= 0 { return Err(ImageSimilarityError { reason: format!("dct_length should be a positive number instead of {}", length)}) } // try to compute phash for `img_a` and `img_b` let phash_img_a = compute_phash(img_a, length, dct_length)?; let phash_img_b = compute_phash(img_b, length, dct_length)?; // compute their hamming distance Ok(hamming_distance(&phash_img_a, &phash_img_b)) } /// Compute similarities of all images with allowed extensions in given directory /// /// # Example /// ```rust /// match similarity_directory("/PATH/TO/A/DIRECTORY", &vec!["png", "jpg", "jpeg"]) { /// Some(result) => println!("{:#?}", result), /// None => println!("No available images with given extensions in the given directory"), /// }; /// ``` pub fn similarity_directory(directory: &str, allowed_ext: &Vec<&str>) -> Option<Vec<(f64, String, String)>> { // compute all phashes in directory with given allowed file extensions let all_image_file = compute_phash_directory(directory, allowed_ext); // the result should be an array of tuple (similarity, image a, image b) let mut result: Vec<(f64, String, String)> = Vec::new(); match all_image_file.len() { // 0 is boring 0 => None, // so is 1 1 => { result.push((1.0, all_image_file[0].0.clone(), all_image_file[0].0.clone())); Some(result) }, _ => { // compute hamming distance for all image pairs for a_index in 0..(all_image_file.len() - 1) { for b_index in (a_index + 1)..all_image_file.len() { let img_a_data = &all_image_file[a_index]; let img_b_data = &all_image_file[b_index]; result.push((hamming_distance(&img_a_data.1, &img_b_data.1), img_a_data.0.clone(), img_b_data.0.clone())); } } // sort by similarity desc result.sort_by(|a, b| b.0.partial_cmp(&a.0).unwrap()); Some(result) } } } /// Compute similarities of given image with all images that ends in allowed extensions in given directory /// /// # Example /// ```rust /// let image = opencv::imgcodecs::imread("/PATH/TO/IMAGE", 0).expect("Invaild image file"); /// match similarity_file_directory(&image, "/PATH/TO/A/DIRECTORY", &vec!["png", "jpg", "jpeg"]) { /// Some(result) => println!("{:#?}", result), /// None => println!("No available images with given extensions in the given directory"), /// }; /// ``` pub fn similarity_file_directory(image: &Mat, directory: &str, allowed_ext: &Vec<&str>) -> Result<Option<Vec<(f64, String)>>, ImageSimilarityError> { let image_phash = compute_phash(&image, 64, 16)?; // compute all phashes in directory with given allowed file extensions let all_image_file = compute_phash_directory(directory, allowed_ext); match all_image_file.len() { // 0 is boring 0 => Ok(None), _ => { // compute hamming distance for all image pairs // the result should be an array of tuple (similarity, image in directory) let mut result: Vec<(f64, String)> = all_image_file.iter().map(|image_data| { (hamming_distance(&image_phash, &image_data.1), image_data.0.clone()) }).collect(); // sort by similarity desc result.sort_by(|a, b| b.0.partial_cmp(&a.0).unwrap()); Ok(Some(result)) } } } /// Compute all phashes in directory with given allowed file extensions /// /// # Example /// ```rust /// println!("{:#?}", compute_phash_directory("/PATH/TO/A/DIRECTORY")); /// ``` fn compute_phash_directory(directory: &str, allowed_ext: &Vec<&str>) -> Vec<(String, String)> { // walk given directory WalkDir::new(directory).into_iter() .filter_map(|e| e.ok()) // keep all ok files .filter_map(|file_entry| { // filter by user given allowed file extensions // store path to the file let filepath = file_entry.path().to_str().unwrap(); // split file path by `.` let parts: Vec<&str> = filepath.split('.').collect(); // check whether the extension is allowed if let Some(_) = allowed_ext.iter().find(|&&ext| ext == parts[parts.len() - 1]) { // keep Some(String::from(filepath)) } else { // no None } }).filter_map(|file| { // with all files with allowed extensions // try to load the file as image let img = match imread(&file, 0) { // proceed next step if successfully opened Ok(img) => img, // otherwise throw this file Err(_) => return None, }; // compute phash of this file with resize length 64 and dct length 16 match compute_phash(&img, 64, 16) { // if nothing goes wrong while computing phash // then return a tuple, (filepath, phash) Ok(phash) => Some((file, phash)), // otherwise throw this file Err(_) => None } }).collect() } /// Compute pHash of given image /// /// # Example /// ```rust /// let image = opencv::imgcodecs::imread("/PATH/TO/IMAGE", 0).expect("Invaild image file"); /// match compute_phash(&image, 64, 16) { /// Ok(phash) => println!("{}", phash), /// Err(e) => println!("{}", e), /// } /// ``` fn compute_phash(img: &Mat, length: i32, dct_length: i32) -> Result<String, ImageSimilarityError> { // we need the image to be grayscale and resized to a reasonable size fn assert_gray_and_size(img: &Mat, length: i32) -> Result<Mat, ImageSimilarityError> { // create a new Mat for the gray image let mut gray = Mat::default()?; // check number of channels of orginal image match img.channels()? { // it's already a grayscale image // just copy it 1 => gray = img.clone()?, // for image with 3 or 4 channels, // convert it to grayscale 3 => cvt_color(&img, &mut gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY, 0)?, 4 => cvt_color(&img, &mut gray, COLOR_RGBA2GRAY, 0)?, // we don't support image with any other number of channels _ => return Err(ImageSimilarityError { reason: format!("Image with {} channels is not supported yet", img.channels().unwrap()) }), }; // create a new Mat for the resized image let mut resized = Mat::default()?; // specific size let size = Size_::new(length, length); // and resize the original image resize(&gray, &mut resized, size, 0.0, 0.0, imgproc::INTER_LINEAR)?; Ok(resized) } // try to get the resized and grayscale image let resized_gray = assert_gray_and_size(&img, length)?; // convert the underlaying type of resized_gray into double let mut double_type_img = Mat::new_rows_cols_with_default(resized_gray.rows()?, resized_gray.cols()?, CV_64FC1, Scalar::new(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0))?; Mat::convert_to(&resized_gray, &mut double_type_img, CV_64FC1, 1.0, 0.0)?; // and then do dct let mut dct_img = Mat::default()?; dct(&double_type_img, &mut dct_img, 0)?; // compute the mean value of dct image let mut mean: f64 = 0.0; for row in 0..dct_length { for col in 0..dct_length { mean += dct_img.at(row + col * length)?; } } // remember to substract the first value of dct mean -= dct_img.at(0)?; mean /= (length * length - 1) as f64; // build the phash string of the given image let mut phash = String::new(); for row in 0..dct_length { for col in 0..dct_length { let value: &f64 = dct_img.at(row + col * length)?; if value < &mean { phash.push_str("0"); } else { phash.push_str("1"); } } } Ok(phash) } /// Compute hamming distance of two given string /// /// # Example /// ```rust /// println!("{}", hamming_distance(&String::from("111"), &String::from("101"))); /// ``` fn hamming_distance(a: &String, b: &String) -> f64 { // get length of two strings let len1 = a.len(); let len2 = b.len(); // we only compute the hamming distance if the lengths are equal, but expect 0 match (len1, len2, len1 - len2) { (_, _, 0) => { let mut dist: f64 = 0.0; for i in 0..len1 { if a.chars().nth(i) != b.chars().nth(i) { dist += 1.0; } } 1.0 - dist / (len1 as f64) }, (0, _, _) => 0.0, (_, 0, _) => 0.0, (_, _, _) => 0.0, } }