A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
The Linked List is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representingNode.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from0ton-1) where random pointer points to, ornullif it does not point to any node.
Example 1:
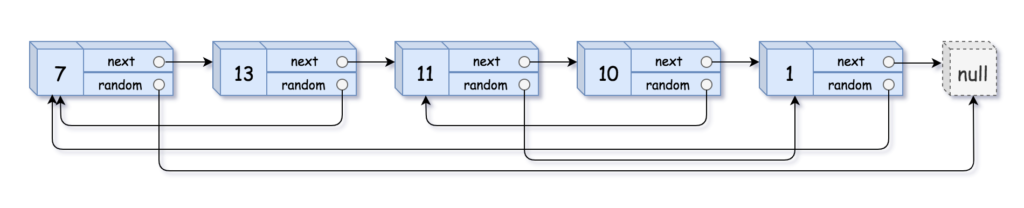
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
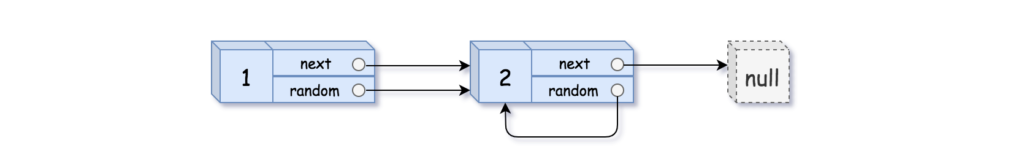
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]] Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
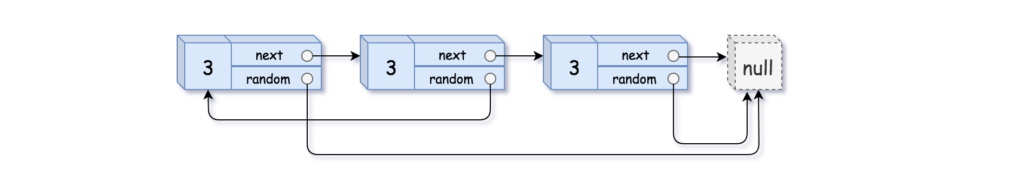
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = [] Output: [] Explanation: Given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.randomis null or pointing to a node in the linked list.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
Solution
#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <vector> class Node { public: int val; Node* next; Node* random; Node(int _val) { val = _val; next = NULL; random = NULL; } }; Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) { // (old) pointer to (new) pointer mapping std::map<Node*, Node*> ptr2ptr; // copy from index 0 int index = 0; // i.e., head Node * copy = head; // head of copy Node * copyHead = nullptr; // previous copy Node * copyPrev = nullptr; // current copy Node * copyCur = nullptr; // if data available while (copy != nullptr) { // copy it copyCur = new Node(copy->val); // if `copyPrev` is not null if (copyPrev) { // save `copyCur` in `next` field of `copyPrev` copyPrev->next = copyCur; } else { // otherwise we're copying the first node // so we save `copyCur` to `copyHead` copyHead = copyCur; } // map old pointer to new pointer ptr2ptr[copy] = copyCur; // current node become previous node copyPrev = copyCur; // increase index by 1 index++; // move to next node copy = copy->next; } // iterate all over again to substitute `random` field // from old pointer to new pointer copy = head; copyPrev = copyHead; while (copy != nullptr) { if (copy->random != nullptr) { // old pointer to new pointer copyPrev->random = ptr2ptr[copy->random]; } copy = copy->next; copyPrev = copyPrev->next; } return copyHead; } int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) { std::vector<Node *> nodes; nodes.push_back(new Node(7)); nodes.push_back(new Node(13)); nodes.push_back(new Node(11)); nodes.push_back(new Node(10)); nodes.push_back(new Node(1)); for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size() - 1; i++) { nodes[i]->next = nodes[i+1]; } nodes[0]->random = nullptr; nodes[1]->random = nodes[0]; nodes[2]->random = nodes[4]; nodes[3]->random = nodes[2]; nodes[4]->random = nodes[0]; copyRandomList(nodes[0]); }